WHAT IS APHASIA?
Aphasia is an acquired communication disorder.
It can affect an individual's ability to:
SPEAK
UNDERSTAND
READ
WRITE
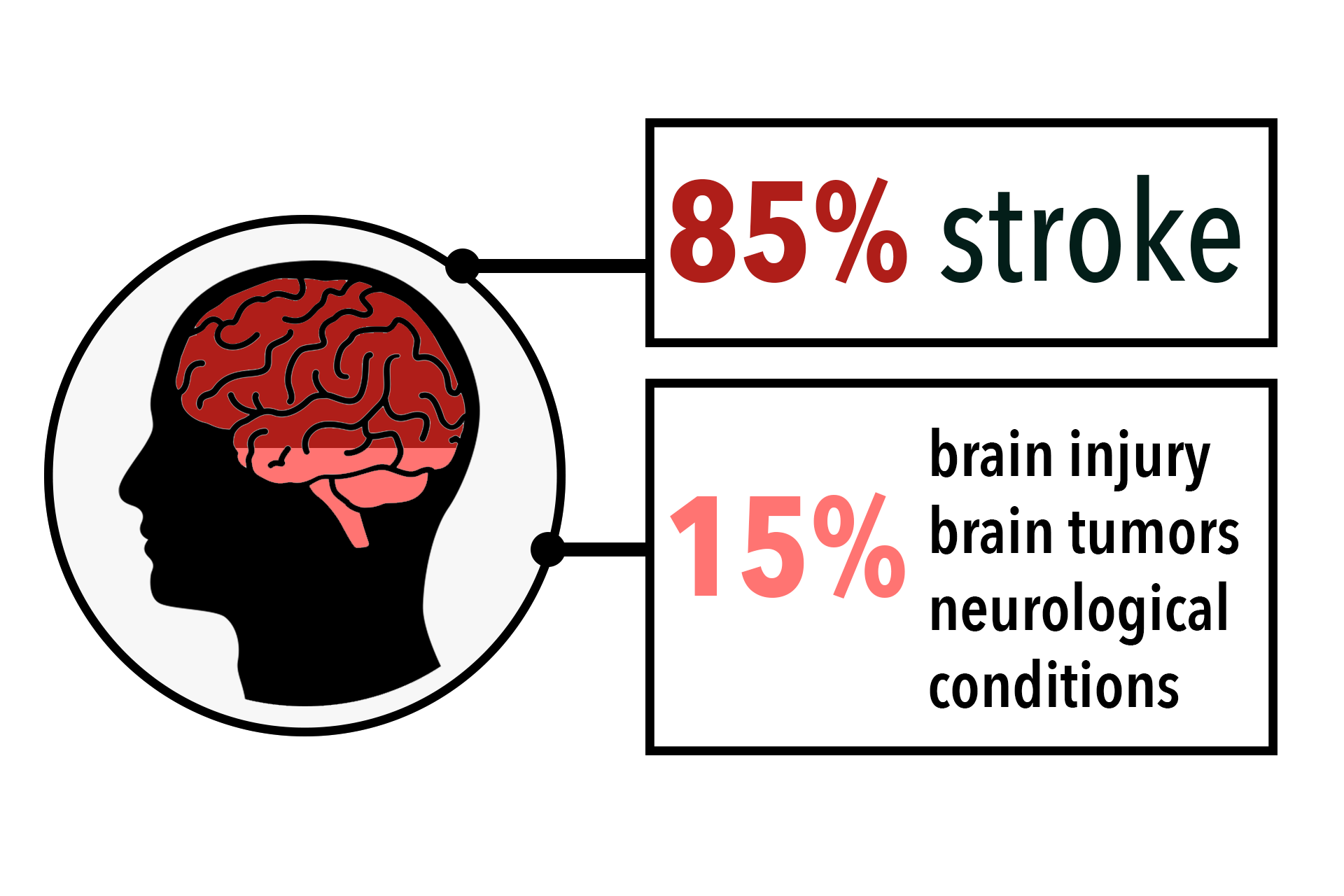
CAUSES OF APHASIA
Aphasia occurs when areas of the brain responsible for language are damaged by stroke, brain injury, brain tumors or neurological disease.
TYPES OF APHASIA
Aphasia can be classified as mild, moderate and severe.
There are several different types of aphasia. However, many people with aphasia present with a mix of both receptive and expressive challenges.
EXPRESSIVE APHASIA
(NON-FLUENT APHASIA)
Expressive aphasia is a partial or total loss of the ability to express oneself through speech and/or writing. You know what you want to say, but struggle to say or write what you mean.
RECEPTIVE APHASIA
(FLUENT APHASIA)
Receptive aphasia reflects difficulty with understanding speech and language. You can speak, but sometimes the speech doesn't make sense, or you may have difficulty making sense of what you hear and/or read.